The Legislative Body
The Legislative Body
Oregon’s bicameral legislature consists of the House of Representatives, which has 60 members elected for two-year terms, and the Senate, whose 30 members are elected to serve for four-year terms.
Oregonians choose their legislators by voting every even-numbered year. The primary election is held on the third Tuesday in May. The general election is held on the first Tuesday (after the first Monday) in November.
Oregon uses a system of single-member districts to elect its legislators. Each of the 90 members represents a designated senatorial or representative district, meaning each Oregonian is represented by a single Senator and a single Representative. Representative districts have a population of about 70,621; Senate districts contain about 141,242 people. These district lines are redrawn every ten years. Find further information about
Senators and
Representatives.
According to the Oregon Constitution, Senators or Representatives must be United States citizens of at least 21 years of age, and residents for at least one year of the legislative district from which they were elected.
In Oregon’s representative form of government, the legislature is integral to the process of proposing, deliberating and setting public policy.
The primary functions of the Legislative Assembly are to enact new laws and revise existing ones relating to the health, education and general welfare of Oregonians, and to make decisions that keep the state in good economic and environmental condition. An informal, but highly significant, function is to provide a forum for resolution of group conflicts and expressions of public grievances. This public/legislative interaction frequently occurs without the enactment of any new laws.
The Legislative Assembly is responsible for the state's biennial budget. The power to allocate state monies gives the legislature influence over the executive branch. In deciding where and how much money the state will spend on its agencies and programs, the legislature establishes priorities and sets public policy.
In addition to enacting laws, setting public policy, and administering the state’s budget, legislators review administrative rules drafted by state agencies. An additional responsibility is the Senate’s confirmation of certain executive appointments made by the Governor.
Legislative Leadership
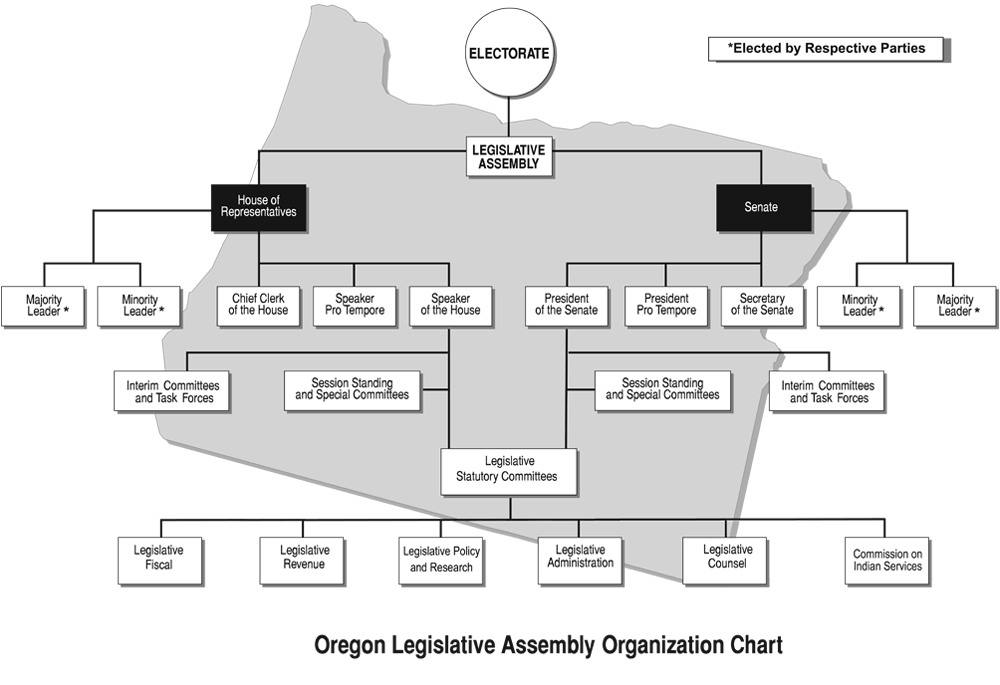
The Speaker of the House and President of the Senate, the two most significant leadership positions in the legislature, are elected by the majority of their respective houses to preside over daily sessions and perform other duties prescribed by rule, custom, and law.
The Speaker and President are empowered to assign members and appoint chairpersons and vice-chairpersons to standing committees. They refer measures to committees and oversee their respective employees.
A Speaker Pro Tempore and President Pro Tempore, who serve as the temporary presiding officers in the absence of the Speaker and President, are also elected.
Each body also elects an officer who is not a legislator to manage internal operations. The Chief Clerk of the House and the Secretary of the Senate provide parliamentary assistance, maintain legislative records and measures, and supervise the personnel managing the legislature’s paper flow.
A Sergeant at Arms is also selected in each chamber to maintain order.
In addition to the official posts of the Legislative Assembly, the minority and majority parties of each body elect a leader to help manage party affairs. The House and Senate Majority and Minority Leaders retain continuing staff to provide constituent relations, public information and general operation services for each caucus.
Legislative Assembly Organization Chart